This guide walks you through the process of creating a simple web application with resources that are protected by Spring Security.
You will build a Spring MVC application that secures the page with a login form that is backed by a fixed list of users.
You can use this pre-initialized project and click Generate to download a ZIP file. This project is configured to fit the examples in this tutorial.
To manually initialize the project:
-
Navigate to https://start.spring.io. This service pulls in all the dependencies you need for an application and does most of the setup for you.
-
Choose either Gradle or Maven and the language you want to use. This guide assumes that you chose Java.
-
Click Dependencies and select Spring Web and Thymeleaf.
-
Click Generate.
-
Download the resulting ZIP file, which is an archive of a web application that is configured with your choices.
|
Note
|
If your IDE has the Spring Initializr integration, you can complete this process from your IDE. |
|
Note
|
You can also fork the project from Github and open it in your IDE or other editor. |
Before you can apply security to a web application, you need a web application to secure. This section walks you through creating a simple web application. Then you will secure it with Spring Security in the next section.
The web application includes two simple views: a home page and a “Hello, World” page.
The home page is defined in the following Thymeleaf template (from
src/main/resources/templates/home.html):
link:initial/src/main/resources/templates/home.html[role=include]This simple view includes a link to the /hello page, which is defined in the following
Thymeleaf template (from src/main/resources/templates/hello.html):
link:initial/src/main/resources/templates/hello.html[role=include]The web application is based on Spring MVC. As a result, you need to configure Spring MVC
and set up view controllers to expose these templates. The following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/securingweb/MvcConfig.java) shows a class that configures
Spring MVC in the application:
link:initial/src/main/java/com/example/securingweb/MvcConfig.java[role=include]The addViewControllers() method (which overrides the method of the same name in
WebMvcConfigurer) adds four view controllers. Two of the view controllers reference
the view whose name is home (defined in home.html), and another references the view
named hello (defined in hello.html). The fourth view controller references another
view named login. You will create that view in the next section.
At this point, you could jump ahead to “Run the Application” and run the application without having to log in to anything.
Now that you have an unsecured web application, you can add security to it.
Suppose that you want to prevent unauthorized users from viewing the greeting page at
/hello. As it is now, if visitors click the link on the home page, they see the greeting
with no barriers to stop them. You need to add a barrier that forces the visitor to sign
in before they can see that page.
You do that by configuring Spring Security in the application. If Spring Security is on the classpath, Spring Boot automatically secures all HTTP endpoints with “basic” authentication. However, you can further customize the security settings. The first thing you need to do is add Spring Security to the classpath.
With Gradle, you need to add two lines (one for the application and one for testing) in
the dependencies closure in build.gradle, as the following listing shows:
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
implementation 'org.springframework.security:spring-security-test'The following listing shows the finished build.gradle file:
link:complete/build.gradle[role=include]With Maven, you need to add two extra entries (one for the application and one for
testing) to the <dependencies> element in pom.xml, as the following listing shows:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>The following listing shows the finished pom.xml file:
link:complete/pom.xml[role=include]The following security configuration (from
src/main/java/com/example/securingweb/WebSecurityConfig.java)
ensures that only authenticated users can see the secret greeting:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/securingweb/WebSecurityConfig.java[role=include]The WebSecurityConfig class is annotated with @EnableWebSecurity to enable Spring
Security’s web security support and provide the Spring MVC integration. It also extends
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter and overrides a couple of its methods to set some specifics
of the web security configuration.
The configure(HttpSecurity) method defines which URL paths should be secured and which
should not. Specifically, the / and /home paths are configured to not require any
authentication. All other paths must be authenticated.
When a user successfully logs in, they are redirected to the previously requested page
that required authentication. There is a custom /login page (which is specified by
loginPage()), and everyone is allowed to view it.
The userDetailsService() method sets up an in-memory user store with a single user. That
user is given a user name of user, a password of password, and a role of USER.
Now you need to create the login page. There is already a view controller for the login
view, so you need only to create the login view itself, as the following listing (from
src/main/resources/templates/login.html) shows:
link:complete/src/main/resources/templates/login.html[role=include]This Thymeleaf template presents a form that captures a username and password and posts
them to /login. As configured, Spring Security provides a filter that intercepts that
request and authenticates the user. If the user fails to authenticate, the page is
redirected to /login?error, and your page displays the appropriate error message. Upon
successfully signing out, your application is sent to /login?logout, and your page
displays the appropriate success message.
Last, you need to provide the visitor a way to display the current user name and sign out.
To do so, update the hello.html to say hello to the current user and contain a
Sign Out form, as the following listing (from src/main/resources/templates/hello.html)
shows:
link:complete/src/main/resources/templates/hello.html[role=include]We display the username by using Spring Security’s integration with
HttpServletRequest#getRemoteUser(). The “Sign Out” form submits a POST to /logout.
Upon successfully logging out, it redirects the user to /login?logout.
The Spring Initializr creates an application class for you. In this case, you need not
modify the class. The following listing (from
src/main/java/com/example/securingweb/SecuringWebApplication.java) shows the application
class:
link:complete/src/main/java/com/example/securingweb/SecuringWebApplication.java[role=include]https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-guides/getting-started-macros/main/build_an_executable_jar_subhead.adoc https://raw.githubusercontent.com/spring-guides/getting-started-macros/main/build_an_executable_jar_with_both.adoc
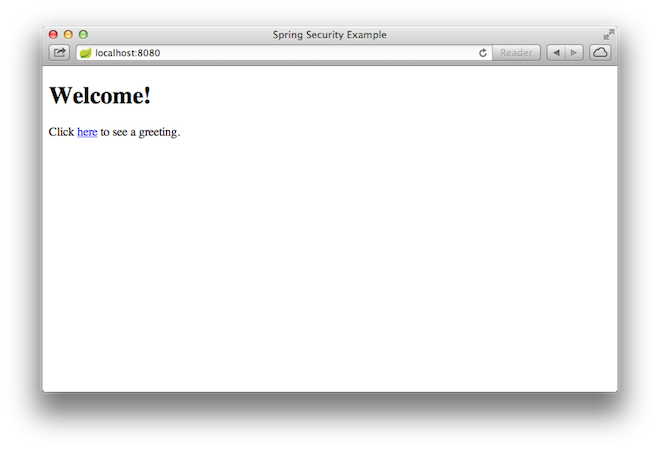
Once the application starts up, point your browser to http://localhost:8080. You should
see the home page, as the following image shows:
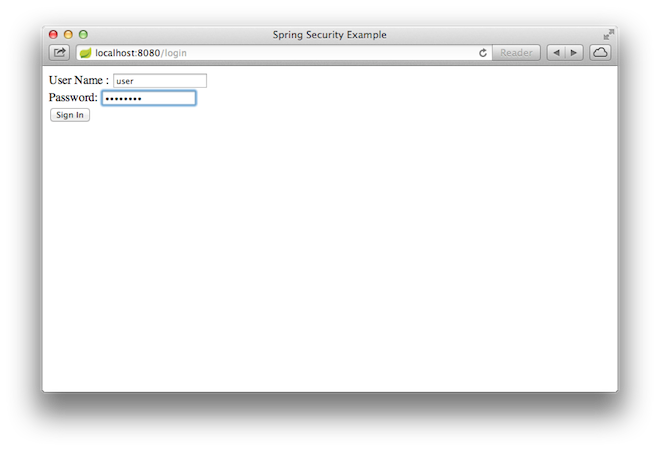
When you click on the link, it attempts to take you to the greeting page at /hello.
However, because that page is secured and you have not yet logged in, it takes you to the
login page, as the following image shows:
|
Note
|
If you jumped down here with the unsecured version, you do not see the login page. You should back up and write the rest of the security-based code. |
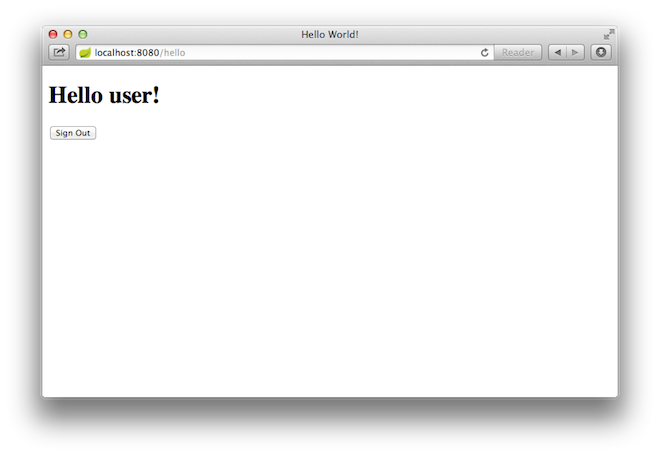
At the login page, sign in as the test user by entering user and password for the
username and password fields, respectively. Once you submit the login form, you are
authenticated and then taken to the greeting page, as the following image shows:
If you click on the Sign Out button, your authentication is revoked, and you are returned to the login page with a message indicating that you are logged out.
Congratulations! You have developed a simple web application that is secured with Spring Security.
The following guides may also be helpful: