|
|
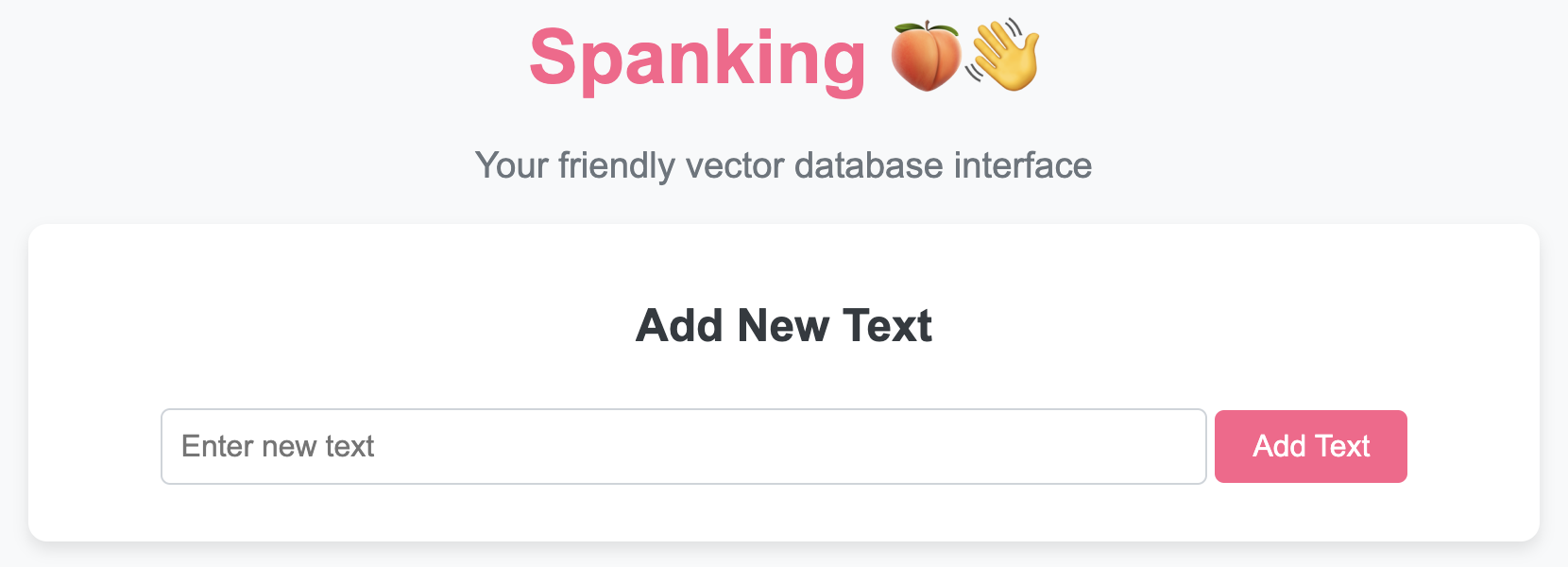
To use the 🍑👋 VectorDB class and access its functionality through a beautiful UI, follow these steps:
First, clone the repository to your local machine:
git clone https://github.com/rishiraj/spanking.git
cd spankingTo manage your vector database through an intuitive web interface, you can run the provided app.py script:
python app.pyThis will start a local web server. You can then access the UI by navigating to http://127.0.0.1:5000 in your web browser.
- Add New Texts: Easily add texts to your vector database through the interface.
- View and Manage Texts: See all stored texts, update them, or delete them with a single click.
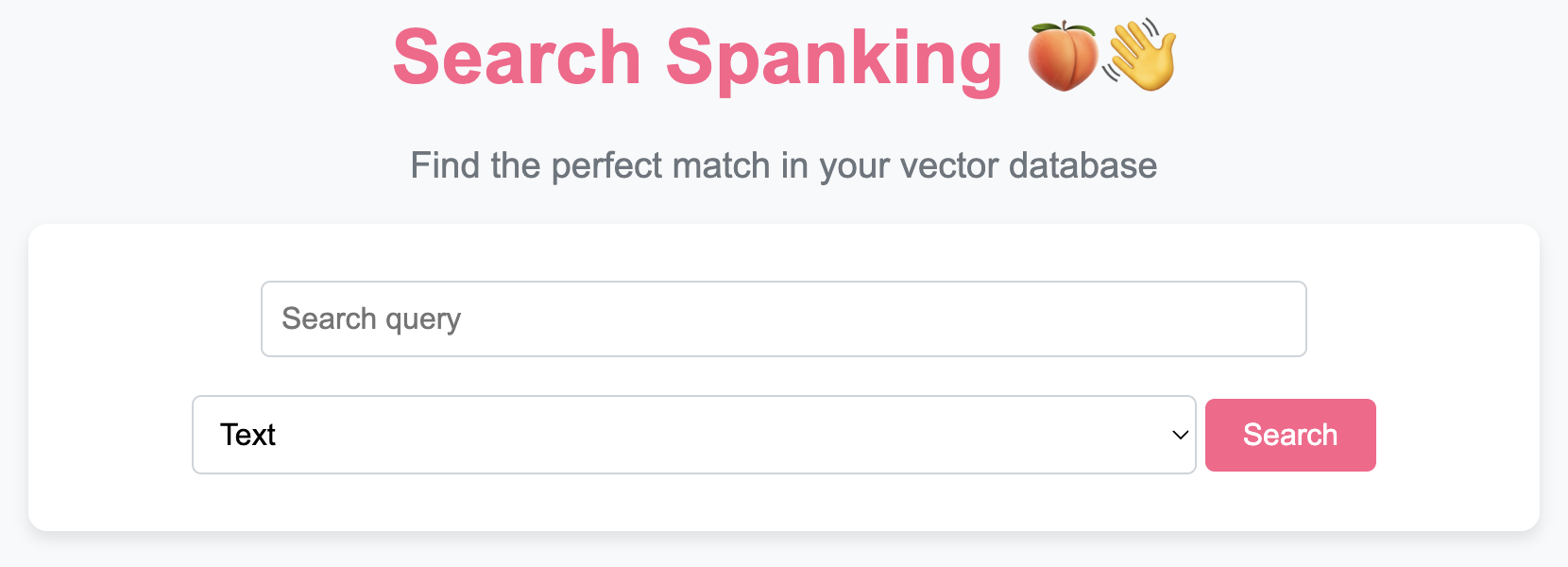
- Search Functionality: Perform text or image-based searches within your database and view the results directly in your browser.
- Save and Load Database: Save your database to a file or load it from a previously saved state with ease.
If you prefer working with code, you can interact with the VectorDB class directly. Here’s how:
-
Create an Instance:
from spanking import VectorDB vector_db = VectorDB(model_name='BAAI/bge-base-en-v1.5')
You can optionally specify a different pre-trained sentence transformer model by passing its name to the constructor.
-
Add Texts:
texts = ["i eat pizza", "i play chess", "i drive bus"] vector_db.add_texts(texts)
This will encode the texts into embeddings and store them in the database.
-
Search for Similar Texts or Images:
text_query = "we play football" text_results = vector_db.search(text_query, top_k=2, type='text') print("Text search results:") for text, similarity in text_results: print(f"Text: {text}, Similarity: {similarity}") image_url = "https://example.com/image.jpg" image_results = vector_db.search(image_url, top_k=2, type='image') print("\nImage search results:") for text, similarity in image_results: print(f"Text: {text}, Similarity: {similarity}")
This will retrieve the top-2 most similar texts or images to the query based on cosine similarity. The
searchmethod returns a list of tuples, where each tuple contains the text and its similarity score. You can specify the search type using thetypeparameter ('text'for text search and'image'for image search). -
Delete a Text:
index = 1 vector_db.delete_text(index)
This will remove the text and its corresponding embedding at the specified index.
-
Update a Text:
index = 0 new_text = "i enjoy eating pizza" vector_db.update_text(index, new_text)
This will update the text and its corresponding embedding at the specified index with the new text.
-
Save the Database:
vector_db.save('vector_db.pkl')
This will save the current state of the
VectorDBinstance to a file named 'vector_db.pkl'. -
Load the Database:
vector_db = VectorDB.load('vector_db.pkl')
This will load the
VectorDBinstance from the file named 'vector_db.pkl' and return it. -
Convert to DataFrame:
df = vector_db.to_df()
This will convert the current state of the
VectorDBinstance to a Pandas Dataframe. -
Iterate Over Stored Texts:
for text in vector_db: print(text)
-
Access Individual Texts by Index:
index = 2 text = vector_db[index] print(text)
-
Get the Number of Texts:
num_texts = len(vector_db) print(num_texts)
Here's an example to demonstrate how you can use the 🍑👋 VectorDB class:
from spanking import VectorDB
vector_db = VectorDB()
# Add texts to the database
texts = ["i eat pizza", "i play chess", "i drive bus"]
vector_db.add_texts(texts)
# Search for similar texts
query = "we play football"
top_results = vector_db.search(query, top_k=2)
print("Top results:")
for text, similarity in top_results:
print(f"Text: {text}, Similarity: {similarity}")
# Update a text
vector_db.update_text(1, "i enjoy playing chess")
# Delete a text
vector_db.delete_text(2)
# Save the database
vector_db.save('vector_db.pkl')
# Load the database
loaded_vector_db = VectorDB.load('vector_db.pkl')
# Iterate over the stored texts in the loaded database
print("\nStored texts in the loaded database:")
for text in loaded_vector_db:
print(text)
# Convert to dataframe
df = loaded_vector_db.to_df()
print(df.head())This example demonstrates how to create a 🍑👋 VectorDB instance, add texts, search for similar texts, update and delete texts, and iterate over the stored texts.
