Typst Sympy Calculator parses Typst Math Expressions and converts it into the equivalent SymPy form. Then, calculate it and convert to typst math text.
It is designed for providing people writing in typst a ability to calculate something when writing math expression. It is based on Sympy module in Python.
The typst-sympy-calculator python package is a backend for a VS Code extension Typst Sympy Calculator, and you also can use it just for parse typst math expression to sympy form in order to do things for yourself.
- Default Math:
- Arithmetic: Add (
+), Sub (-), Dot Mul (dot), Cross Mul (times), Frac (/), Power (^), Abs (|x|), Sqrt (sqrt), etc... - Alphabet:
a - z,A - Z,alpha - omega, Subscript (x_1), Accent Bar(hat(x)), etc... - Common Functions:
gcd,lcm,floor,ceil,max,min,log,ln,exp,sin,cos,tan,csc,sec,cot,arcsin,sinh,arsinh, etc... - Funcion Symbol:
f(x),f(x-1,),g(x,y), etc... - Calculous: Limit
lim_(x -> oo) 1/x, Integrationintegral_1^2 x dif x, etc... - Calculous: Derivation (
dif/(dif x) (x^2 + 1)is not supported, but you can usederivative(expr, var)instead), etc... - Reduce: Sum
sum_(k=1)^oo (1/2)^k, Productproduct_(k=1)^oo (1/2)^k, etc... - Eval At: Evalat
x^2 bar_(x = 2),x^2 "|"_(x = 2), etc... - Linear Algebra: Matrix to raw echelon form
rref, Determinantdet, Transpose^T, Inverse^(-1), etc... - Relations:
==,>,>=,<,<=, etc... - Solve Equation: Single Equation
x + 1 = 2, Multiple Equationscases(x + y = 1, x - y = 2), etc... - Logical:
and,or,not, etc... - Set Theory:
in,sect,union,subset, etc... - Other: Binomial
binom(n, k)...
- Arithmetic: Add (
- Custom Math (in typst file):
- Define Accents:
#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave) - Define Operators:
#let add = math.op("add") - Define Symbols:
#let xy = math.italic("xy")or#let mail = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),) - Define Functions:
# typst-calculator @func() def convert_add(a, b): return a + b
- Define Accents:
- Typst Math Printer:
- Complete
TypstMathPrinterinTypstConverter.py - Custom Printer for
TypstCalculator.pyandTypstCalculatorServer.py
- Complete
- VS Code Extension:
- Develop a VS Code Extension for
Typst Calculator
- Develop a VS Code Extension for
pip install typst-sympy-calculatorTypstParser.py: parse typst math expression to ANTLR abstract syntax tree withTypstGrammar.g4;TypstConverter.py:- convert typst math expression to sympy expression via
TypstMathConverter; - convert sympy expression to typst math expression via
TypstMathPrinter; - has
decoratorsfor defining custom functions, operators; - has
define_accent,define_symbol_baseanddefine_functionfor defining custom accents, symbols and functions;
- convert typst math expression to sympy expression via
TypstCalculator.py:- calculate sympy expression and convert to typst math expression;
- has
subs,simplify,evalfmethods; - has
set_varianceandunset_variancefor calculating with variance;
DefaultTypstCalculator: define many useful functions, operators, accents, symbols;- Accents, Alphabet, Greeks, Arithmetic, Common Functions, Calculous, Linear Algebra, etc...
TypstCalculatorServer:- has
initmethod for initializingTypstCalculatorwith a typst file; - can define your custom functions on your typst file;
- has
simplify,subs,evalfmethods for calculating with typst file;
- has
It is a top-down design, so you can use TypstCalculatorServer directly, or use TypstCalculator with TypstConverter.
RECOMMEND: see the usage of decorators like @func() in DefaultTypstCalculator.py.
For the usage, you can see the unit test part if __name__ == '__main__': in each files.
from TypstCalculatorServer import TypstCalculatorServer
server = TypstCalculatorServer()
typst_math = r'1 + 1'
expr = server.sympy(typst_math)
print(server.typst(expr))from TypstCalculator import TypstCalculator
calculator = TypstCalculator()
typst_math = r'1 + 1'
expr = calculator.sympy(typst_math)
print(calculator.typst(expr))from TypstConverter import TypstMathConverter
converter = TypstMathConverter()
typst_math = r'1 + 1'
expr = converter.sympy(typst_math)
print(converter.typst(expr))The simplest way to use it is just like TypstCalculatorServer.py:
from TypstCalculatorServer import TypstCalculatorServer
server = TypstCalculatorServer()
typst_file = os.path.abspath(r'./tests/test.typ')
server.init(typst_file)
server.return_text = True # otherwise just return sympy form
expr = server.simplify('1 + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # 2
server.enable_subs = False
expr = server.simplify('a + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # a + 1
server.enable_subs = True
expr = server.simplify('a + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # 2
expr = server.simplify('b + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # a + 2
expr = server.simplify('cmat(1, 2)', typst_file)
print(expr) # mat(1; 2)
expr = server.simplify('f(1) + f(1)', typst_file)
print(expr) # 2 f(1)
expr = server.simplify('xy + mail + mail.stamped', typst_file)
print(expr) # mail + mail.stamped + xy
expr = server.solve('x + y + z = 1')
print(expr) # y = -x - z + 1, z = -x - y + 1, x = -y - z + 1
expr = server.solve('cases(x + y + z = 1, x = 2)')
print(expr) # cases(x = 2, z = -y - 1), cases(y = -z - 1, x = 2), y = -x - z + 1, z = -x - y + 1
expr = server.solve('cases(x^2 + y = 4, y = 2)')
print(expr) # x = sqrt(4 - y), cases(y = 2, x = sqrt(2)), cases(y = 2, x = -sqrt(2)), x = -sqrt(4 - y)
expr = server.solve('cases(x < 2, x > 1)')
print(expr) # 1 < x and x < 2and the typst files tests/test.typ
#import "cal.typ": *
// set variances
#let a = 1
#let b = $a + 1$and tests/cal.typ just like:
// define accents
#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave)
// define operators
#let add = math.op("add")
#let f = math.op("f")
// define symbols
#let xy = math.italic("xy")
#let mail = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),)If you have not a typst file, you can use DefaultTypstCalculator.py, it define many useful functions and symbols just like:
# Symbols
abc = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
for c in abc:
calculator.define_symbol_base(c)
calculator.define_symbol_base(c.upper())
# Functions
@func()
def convert_sin(expr):
return sympy.sin(expr)So you can use it by:
from DefaultTypstCalculator import get_default_calculator
calculator = get_default_calculator(complex_number=True)
calculator.return_text = True
operator, relation_op, additive_op, mp_op, postfix_op, \
reduce_op, func, func_mat, constant = calculator.get_decorators()
expr = calculator.simplify('1 + 1')
assert expr == '2'
expr = calculator.evalf('1/2', n=3)
assert expr == '0.500'
calculator.set_variance('a', '1/2')
expr = calculator.simplify('a + 1')
assert expr == '3/2'
calculator.unset_variance('a')
expr = calculator.simplify('a + 1')
assert expr == 'a + 1' or expr == '1 + a'
expr = calculator.evalf('pi', n=3)
assert expr == '3.14'
expr = calculator.simplify('max(1, 2)')
assert expr == '2'
calculator.define_function('f')
expr = calculator.simplify('f(1) + f(1) - f(1)')
assert expr == 'f(1)'
expr = calculator.simplify('lim_(x -> oo) 1/x')
assert expr == '0'You can ASSIGN variance a value using same assignment form in typst:
#let x = 1
// Before
$ x $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ x = 1 $PS: You can use grammar like y == x + 1 to describe the relation of equality.
If you want to see the bonding of variances, you can press Shift + Ctrl + P, and input typst-sympy-calculator: Show Current variances, then you will get data like:
y = x + 1
z = 2 xYou can DEFINE a function using same form in typst:
#let f = math.op("f")
// Before
$ f(1) + f(1) $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ f(1) + f(1) = 2 f(1) $You can DEFINE a symbol using same form in typst:
#let xy = math.italic("xy")
#let email = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),)
$ xy + email + email.stamped $You can DEFINE a accent using same form in typst:
#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave)
$ acc(x) $You can DEFINE a operator using same form in typst:
#let add = math.op("+")
'''typst-calculator
@additive_op()
def convert_add(a, b):
return a + b
'''
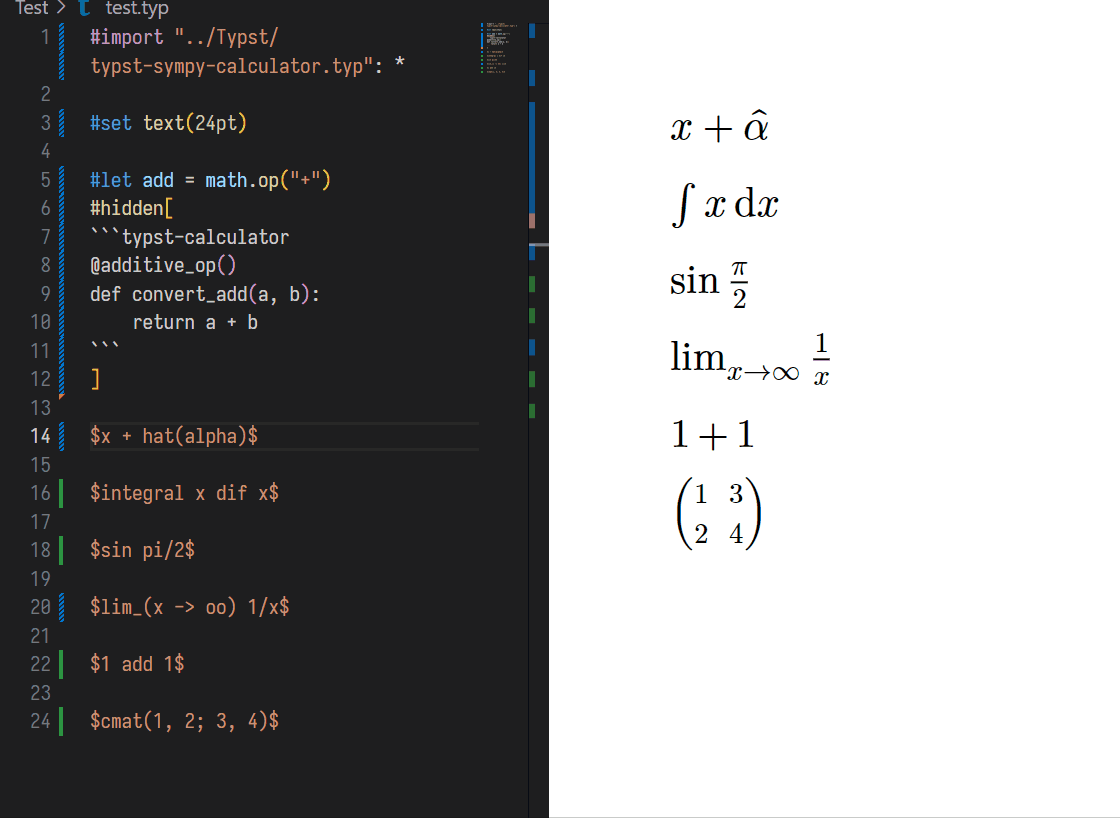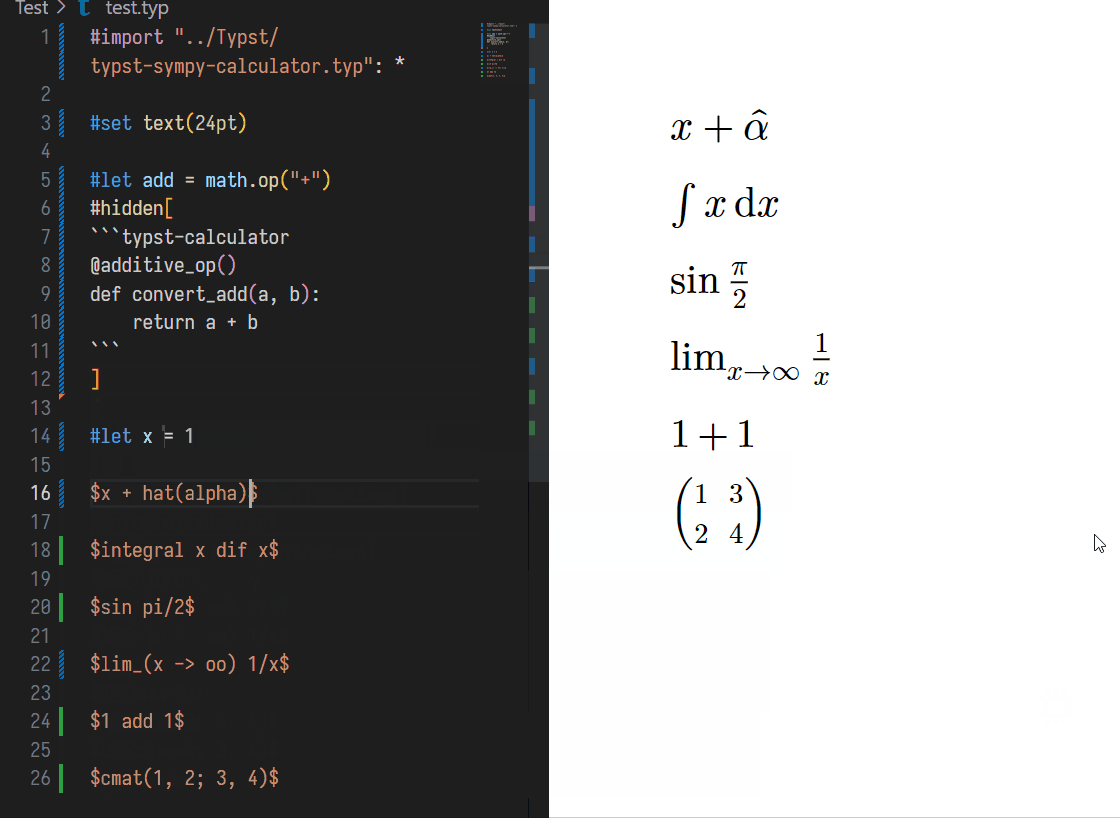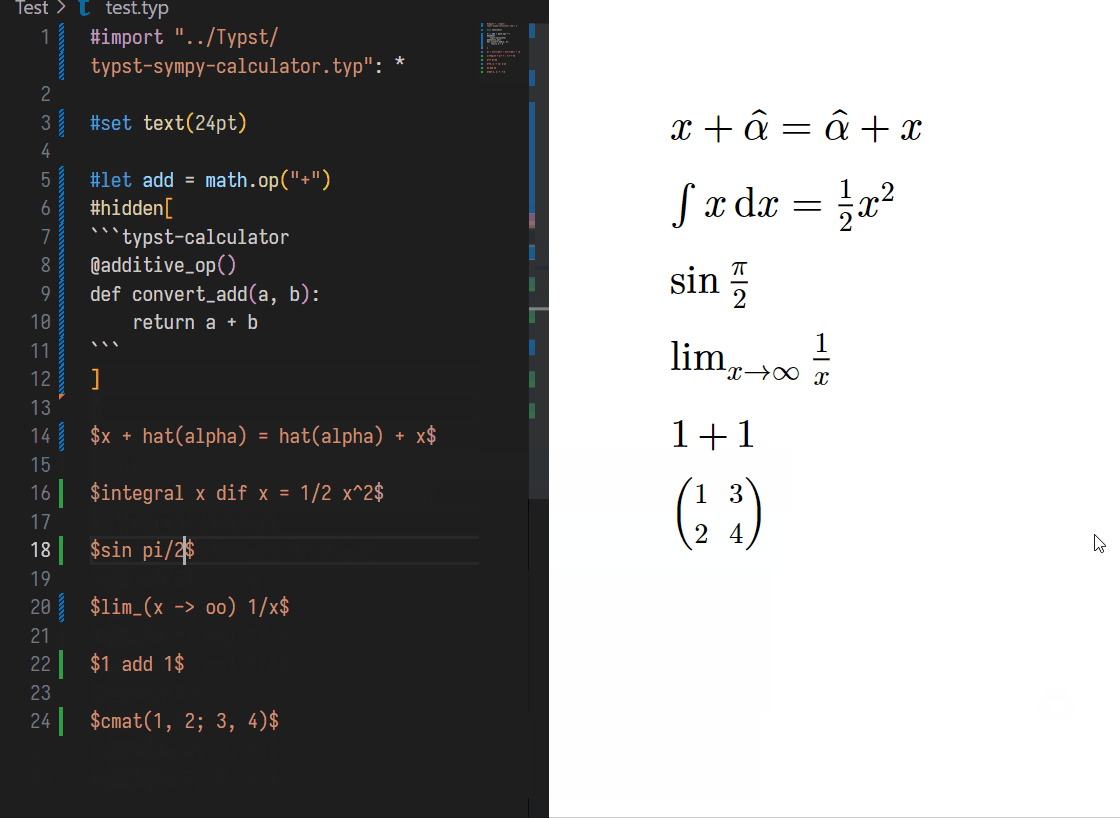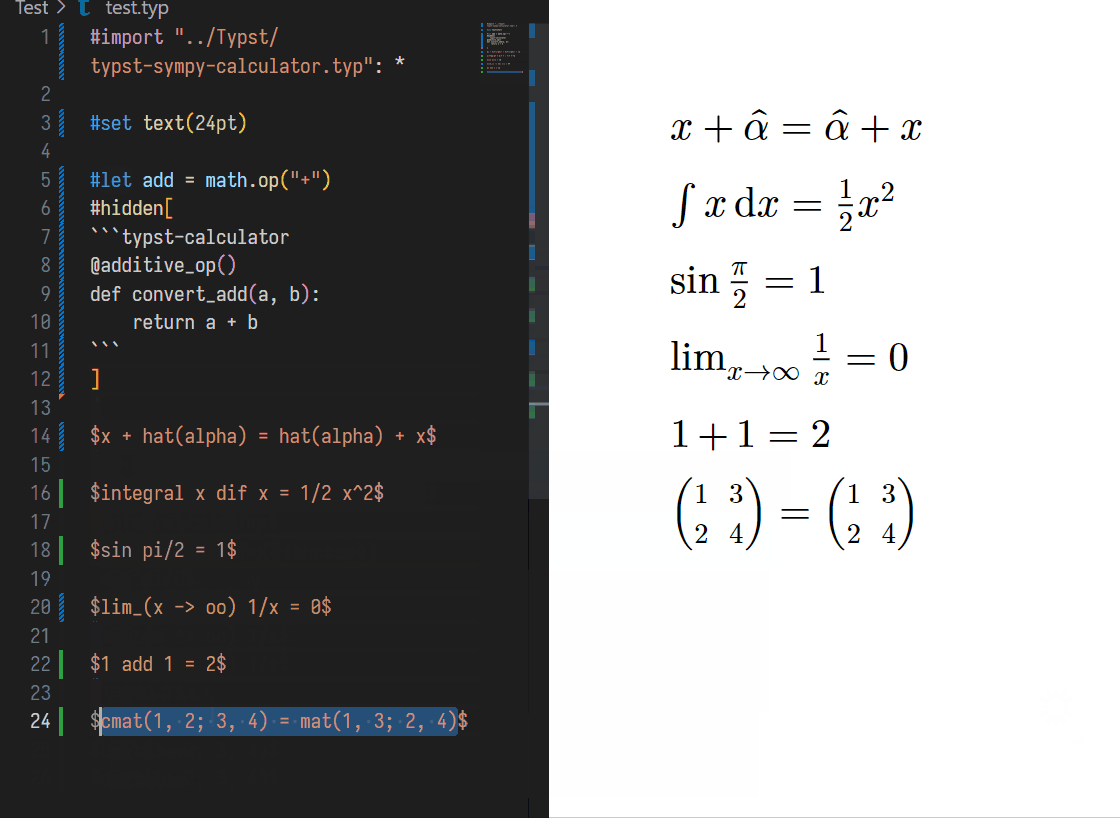
// Before
$ 1 add 1 $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ 1 add 1 = 2 $Or just use '''typst-sympy-calculator or '''python \n # typst-calculator to define a operator.
there are some decorators you can use:
@operator(type='ADDITIVE_OP', convert_ast=convert_ast, name=name, ast=False): Define a common operator;@func(): Define a function, receive args list;@func_mat(): Define a matrix function, receive single argmatrix;@constant(): Define a constant, receive no args but only return a constant value;@relation_op(): Define a relation operator, receive argsaandb;@additive_op(): Define a additive operator, receive argsaandb;@mp_op(): Define a multiplicative operator, receive argsaandb;@postfix_op(): Define a postfix operator, receive argsa;@reduce_op(): Define a reduce operator, receive argsexprandargs = (symbol, sub, sup);
It is important that the function name MUST be def convert_{operator_name}, or you can use decorator arg @func(name='operator_name'), and the substring _dot_ will be replaced by ..
There are some examples (from DefaultTypstCalculator.py):
# Functions
@func()
def convert_binom(n, k):
return sympy.binomial(n, k)
# Matrix
@func_mat()
def convert_mat(mat):
return sympy.Matrix(mat)
# Constants
@constant()
def convert_oo():
return sympy.oo
# Relation Operators
@relation_op()
def convert_eq(a, b):
return sympy.Eq(a, b)
# Additive Operators
@additive_op()
def convert_plus(a, b):
return a + b
# Mp Operators
@mp_op()
def convert_times(a, b):
return a * b
# Postfix Operators
@postfix_op()
def convert_degree(expr):
return expr / 180 * sympy.pi
# Reduces
@reduce_op()
def convert_sum(expr, args):
# symbol, sub, sup = args
return sympy.Sum(expr, args)- Clone it by
git clone https://github.com/OrangeX4/typst-calculator.git - Install dependencies by
pip install -r requirements.txt - Compile ANTLR grammar by
python ./scripts/compile.py - Debug or add your code with
TypstCalculatorServer.pyorTypstCalculator.py, etc...
It is welcome to create an issue or pull request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.