Motivation for Linear Algebra in Data Science
Introduction
Algebra & Statistics are founding steps for data science & machine learning. Machine learning is as much about linear algebra, probability theory and statistics (especially graphical models) and information theory as much as data analysis. In this section of the course, we will focus at Linear Algebra, which is a pre-requisite for almost any technical field of knowledge today in about any technical discipline, including computer science and data science. This lesson attempts to present a quick motivation on how and why linear algebra is a valuable skills for data analysts.
Objectives
You will be able to:
- Understand and state the importance of linear algebra in the fields of data science and machine learning
- Describe the areas in AI and machine learning where Linear Algebra might be used for advanced analytics
Background
Linear Algebra is a continuous form of mathematics and is applied throughout science and engineering because it allows you to model natural phenomena and to compute them efficiently. Because it is a form of continuous and not discrete mathematics, a lot of computer scientists don't have a lot of experience with it. Linear Algebra is also central to almost all areas of mathematics like geometry and functional analysis. Its concepts are a crucial prerequisite for understanding the theory behind Data Science. You don't need to understand Linear Algebra before getting started in Data Science, but at some point, you may want to gain a better understanding of how the different Machine Learning algorithms really work under the hood. So if you really want to be a professional in this field, you will have to master the parts of Linear Algebra that are important for Machine Learning.
You might already know a number of linear algebraic concepts and operations like matrix multiplication, calculating determinants, cross-products and eigenvectors/eigenvalues etc (don't worry if you don't, we will cover these in the course). As a data scientist, it is imperative that you carry a theoretic, as well as a practical understanding of these and other similar concepts alongside their applications in real world problem solving.
An Analogy
Think of a simple example where you first learn about a sine function as an infinite polynomial while learning trigonometry. Students normally practice this function by passing different values to it and getting the expected results, and manage to relate this to triangles and vertices. When learning advanced physics, students get to learn more applications of sine and other similar functions in the area of sound and light. In the domain of Signal Processing for 1D data, these functions pop up again to help you solve filtering, time-series related problems. An introduction to numeric computation around sine functions can not alone help you understand its wider application areas. In fact sine functions are everywhere in the universe from music to light/sound/radio waves, from pendulum oscillations to alternating current.
## Why Linear Algebra?
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning vector spaces and linear relationships between such spaces. It includes the study of lines, planes, and subspace, but is also concerned with properties common to all vector spaces.
Analogous to the example we saw above, It is important that a data scientist understands how data structures are built with vectors and matrices following the geometric intuitions that are from linear algebra, in addition to the numeric calculations. Such data-focused understanding of linear algebra is what let's machine learning practitioners decide what tools can be applied to a given problem, how to interpret the results of experiments, whereas a numeric understanding helps towards the applications of these tools.
A good understanding of Linear Algebra is necessary to analyze ML/AI algorithms, especially for Deep Learning where so much happens behind the scenes.
Following are some of the areas where linear algebra is commonly practiced in the domain of data science and machine learning.
Computer Vision / Image Processing
So we know that computers are designed to process binary information only, i.e. only 0s and 1s. So how can an image such as Einstein's face above with multiple attributes like color be stored in a computer? This is achieved by storing the pixel intensities for red, blue and green colors in a matrix format. Color intensities can be coded into this matrix and can be processed further for analysis and enhancement related tasks. So any operation which we perform on this image would likely use Linear Algebra with matrices at the back end.
Deep Learning - Tensors
Deep Learning is a sub-domain of machine learning, concerned with algorithms that can imitate the functions and structure of a biological brain as a computational algorithm. These are called the artificial neural networks (ANNs).
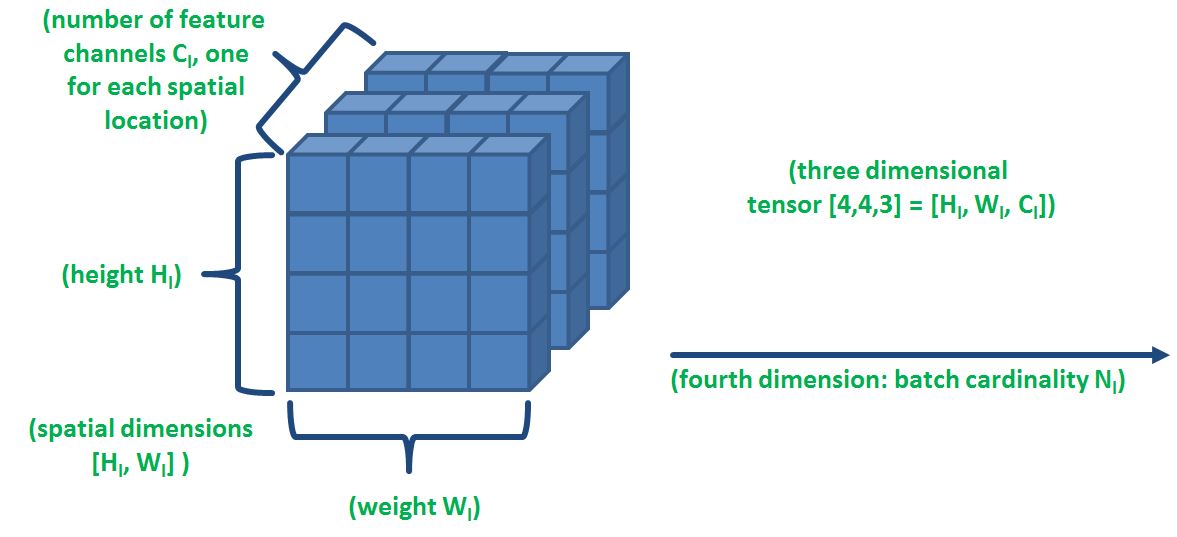
The algorithms usually store and process data in form of mathematical entities called tensors. A tensor is often thought of as a generalized matrix. That is, it could be a 1-D matrix (a vector is actually such a tensor),a 2-D matrix (like a data frame), a 3-D matrix (something like a cube of numbers), even a 0-D matrix (a single number), or a higher dimensional structure that is harder to visualize.
As shown in the image above where different input features are being extracted and stored as spatial locations inside a tensor which appears as a cube. A tensor encapsulates the scalar, vector and the matrix characteristics. For deep learning, creating and processing tensors and operations that are performed on these also require knowledge of linear algebra.
Natural Language Processing
NLP is another active area in Machine Learning is dealing with text data. The most common techniques employed in NLP include BoW (Bag of Words) representation, Term Document Matrix etc. As shown in the image below, words in documents 1,2 and 3 , and their relations are being encoded as numbers and stored in a matrix format.
NLP techniques work in a very similar manner to store counts (or something similar) of words found in different documents. These counts are store in a Matrix form to perform tasks like Semantic analysis, Language translation, Language generation etc.
Dimensionality Reduction
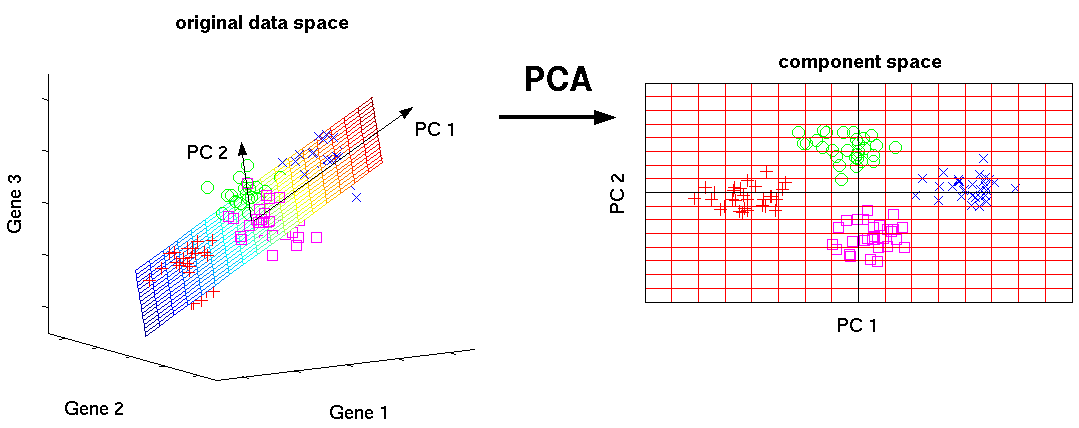
Dimensionality reduction techniques which are heavily employed in the field of big data, use matrices to process data in order to reduce its dimensions. Principle Component Analysis (PCA) is a widely used dimensionality reduction technique, relies solely on calculating Eigenvectors and Eigenvalues to identify principle components, as a set of highly reduced dimensions. The picture below is an example of a three dimensional data being mapped into two dimensions using matrix manipulations.
OK , that makes sense. So what is involved ?
We can have some ideas on whats involved in field of linear algebra by having a quick glance at the word-cloud below that attempts to highlight key linear algebraic terms.
We'll go through an introductory series of lessons and labs that will cover basic ideas of linear algebra: an understanding of vectors and matrices with some basic operations that can be performed on these mathematical entities. We will implement these ideas in python, in an attempt to give you foundation knowledge towards dealing with these algebraic entities and their properties. These skills will be applied in advanced machine learning sections later in the course.
Further Reading
Boost your data science skills. Learn linear algebra.
Quora: Applications of Linear Algebra in Deep Learning
Summary
In this lesson, we worked towards developing a motivation for learning linear algebra for data analysis and machine learning. We looked at some use cases in practical machine learning problems where linear algebra and matrix manipulation might come in handy. In the following lessons, we will look at some of these manipulations, working our way towards solving a regression problem using linear algebraic operations only.