Fork and clone the lab and open the project in IntelliJ.
The lab repository has the required dependencies defined in pom.xml
and the database configuration is defined in persistence.xml.
- Use pgAdmin to create a new database named
jpalab_db:
- Check
persistence.xml(located in src/main/resources/META-INF) to confirm thehibernate.hbm2ddl.autoproperty is set tocreate. - Check
persistence.xmlto confirm thehibernate.show_sqlproperty is set to false. You can change this to true if you prefer to see the SQL statements printed to the output, or leave it as false if you only want to see the Java output.
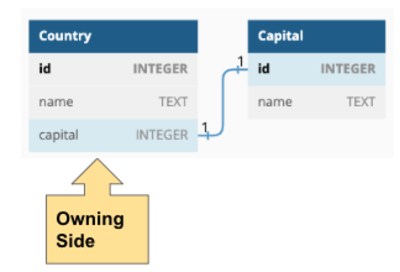
You are given the following entity relationship model:
There is a one-to-one relationship between Country and Capital.
A country has one capital city and a capital city belongs to one country.
You can see from the ERD that Country is assigned to be the owning side of the relationship
since it stores a foreign key reference to Capital.
Open the Country class in the IntelliJ editor. Notice it has a field for the capital along with getter and setter methods:
private Capital capital;Open the Capital class. It has a field for the country along with getter and setter methods.
private Country country;Each class defines a field to reference the other class. However, neither class is using JPA to establish the one-to-one relationship that must be stored in the database.
Try running the JpaCreate.main method to create the lab schema and populate the tables.
Unfortunately, the program will fail because the relationship
between Country and Capital has not been established using JPA. If you scroll through the
errors, you'll see a message about the missing mapping between Capital and Country:
...
at org.example.JpaCreate.main(JpaCreate.java:30)
Caused by: org.hibernate.MappingException: Could not determine type for: org.example.model.Capital, at table: Country, for columns: [org.hibernate.mapping.Column(capital)]
....
You will update the code to add the @OneToOne annotations with appropriate properties
to implement the relationship between Country and Capital.
We will make Country the owner of the one-to-one relationship. That means Capital
is on the non-owning side and must use the mappedBy attribute to establish the bidirectional relationship.
- Edit the
Countryclass and add the@OneToOneannotation for thecapitalfield.
Set thefetchproperty toFetchType.LAZYand set thecascadeproperty toCascadeType.REMOVE. - Edit the
Capitalclass and add the@OneToOneannotation for thecountryfield.
SinceCapitalis on the non-owning side, set themappedByproperty to thecapitalfield that was assigned in theCountryclass. - Run the
JpaCreate.mainmethod. The code should create two tablesCOUNTRYandCAPITAL.
Use the pgAdmin query tool to query the tables.
SELECT * FROM CAPITAL;
| ID | NAME |
|---|---|
| 3 | Paris |
| 4 | Mexico City |
SELECT * FROM COUNTRY;
| ID | NAME | CAPITAL_ID |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | France | null |
| 2 | Mexico | null |
Notice the one-to-one association is stored as the column CAPITAL_ID within the COUNTRY table
(i.e. the entity on the owning side of the relation). However, the column contains null values
because we have not yet called the setCapital method in JpaCreate to establish the relationship
between objects.
-
Edit
JpaCreateto set the capital for each country as shown below:// create country-capital associations country1.setCapital(capital1); country2.setCapital(capital2);
-
Run the
JpaCreate.mainmethod to recreate the tables with the associations. -
Use pgAdmin to query the tables:
SELECT * FROM CAPITAL;
| ID | NAME |
|---|---|
| 3 | Paris |
| 4 | Mexico City |
SELECT * FROM COUNTRY;
| ID | NAME | CAPITAL_ID |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | France | 3 |
| 2 | Mexico | 4 |
- Change the
hibernate.hbm2ddl.autoproperty in thepersistence.xmltononebefore performing read operations. We will query data in theJpaReadclass using the getter methods. - Edit the
JpaReadclass and add the following code to get and print the countries and capitals:
package org.example;
import org.example.model.Capital;
import org.example.model.Country;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
public class JpaRead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create EntityManager
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("example");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
// get country data using primary key id=1 (France)
Country country1 = entityManager.find(Country.class, 1);
System.out.println(country1);
// get the country's capital
Capital capital1 = country1.getCapital();
System.out.println(capital1);
// get the capital using primary key id=4 (Mexico City)
Capital capital2 = entityManager.find(Capital.class, 4);
System.out.println(capital2);
// get the capital's country
Country country2 = capital2.getCountry();
System.out.println(country2);
// close entity manager and factory
entityManager.close();
entityManagerFactory.close();
}
}Run JpaRead.main and confirm the output:
Country{id=1, name='France'}
Capital{id=3, name='Paris'}
Capital{id=4, name='Mexico City'}
Country{id=2, name='Mexico'}
Edit JpaDelete to delete the country with id 1. This should also cascade the deletion of the capital with id 3
since you set the cascade property for the capital field to CascadeType.REMOVE.
package org.example;
import org.example.model.Country;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.EntityManagerFactory;
import javax.persistence.EntityTransaction;
import javax.persistence.Persistence;
public class JpaDelete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create EntityManager
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("example");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
// get record
Country country1 = entityManager.find(Country.class, 1);
// access transaction object
EntityTransaction transaction = entityManager.getTransaction();
// create and use transaction to save updated value
transaction.begin();
entityManager.remove(country1);
transaction.commit();
// close entity manager
entityManager.close();
entityManagerFactory.close();
}
}Use pgAdmin to query the tables and confirm the deletion:
SELECT * FROM CAPITAL;
| ID | NAME |
|---|---|
| 4 | Mexico City |
SELECT * FROM COUNTRY;
| ID | NAME | CAPITAL_ID |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Mexico | 4 |
Save all files before submitting your project.