Create a chatbot using Alexa-style skills and intents.
$ npm install chatskillsChatskills is a quick and easy way to create a conversational user-interface for applications and services. It uses a collection of skills and intents, styled after the Alexa Skills Kit, to setup matching phrases and logic for responding to user requests.
Chatskills does not require a server and can run directly in the console. It can also run on the web. It handles requests from multiple users and maintains session memory. When a user starts a conversation with one of the skills, the skill continues to execute within a session context, until the skill terminates.
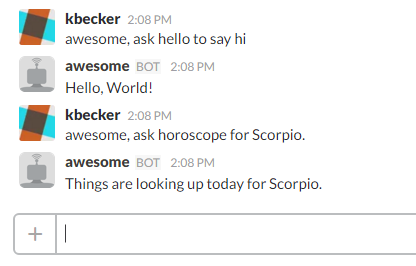
> chatskills, ask hello to say hi.
Hello, World!
> chatskills, ask horoscope for Scorpio.
Things are looking up today for Scorpio.
> chatskills, ask funny to tell me a joke
Knock knock.
> who's there?
Banana.
> banana who
Knock knock.
> whos there
Orange.
> orange who?
Orange you glad I didn't say banana?
In this example, the user accesses three different skills: hello, horoscope, and funny.
Using chatskills is easy. Add a new skill, then create some intents. Here's a simple example.
var chatskills = require('chatskills');
// Create a skill.
var hello = chatskills.add('hello');
// Create an intent.
hello.intent('helloWorld', {
'slots': {},
'utterances': [ '{to |}{say|speak|tell me} {hi|hello|howdy|hi there|hiya|hi ya|hey|hay|heya}' ]
},
function(req, res) {
res.say('Hello, World!');
}
);
// Respond to input.
chatskills.respond('chatskills, ask hello to say hi', function(response) {
console.log(response);
});In the above example, the utterances grammar automatically expands to match on the following phrases:
helloWorld to say hi
helloWorld say hi
helloWorld to speak hi
helloWorld speak hi
helloWorld to tell me hi
helloWorld tell me hi
helloWorld to say hello
helloWorld say hello
helloWorld to speak hello
helloWorld speak hello
helloWorld to tell me hello
helloWorld tell me hello
helloWorld to say howdy
...
To interact with the chatbot using this skill, say any of the target phrases. In the above example, we've used the phrase "to say hi", but you can match against any of the generated phrases. For example:
> chatskills, ask hello to tell me hi
Hello, World!
> chatskills, ask hello to say hello
Hello, World!
> chatskills, ask hello to say howdy
Hello, World!
To create a chatbot that runs locally on the console, just include a loop for reading input.
var readlineSync = require('readline-sync');
// Console client.
var text = ' ';
while (text.length > 0 && text != 'quit') {
text = readlineSync.question('> ');
// Respond to input.
chatskills.respond(text, function(response) {
console.log(response);
});
}If you're using async calls in your skills (such as request, etc) then you'll want to use an async loop, instead of the while loop above. Here's an example.
You don't have to use just the console! You can run your chatbot anywhere, like Slack. See here for full example.
var SlackBot = require('slackbots');
var bot = new SlackBot({ token: token, name: 'awesome' });
// Listen to slack messages.
bot.on('message', function(message) {
// Reply to humans.
if (message.type == 'message' && message.text && message.subtype != 'bot_message') {
var author = getUserById(message.user);
var channel = getChannelById(message.channel);
// Respond to input, use author.name as the session id.
chatskills.respond(message.text, author.name, function(response) {
if (channel) {
// Public channel message.
bot.postMessageToChannel(channel.name, response);
}
else {
// Private message.
bot.postMessageToUser(author.name, response);
}
});
}
});Skills are programs that your chatbot can run. They consist of intents, which are composed of utterances (phrases to match from the user input), responses, and session memory. Each skill can access session memory, so you can store and retrieve variables to help with responding intelligently to the user.
Here's an example of creating a new skill, named "horoscope".
var horoscope = chatskills.add('horoscope');Skills are made up of intents. This is where input from the user is matched against an array of utterances. When a match is found, that intent is executed. An intent can get/set variables in the user session by calling req.get('variable') and req.set('variable', value). An intent can output a response by calling res.say('hello').
Here's an example of creating a new intent for the skill "horoscope".
horoscope.intent('predict', {
'slots': {'SIGN':'LITERAL'},
'utterances': [ 'for {signs|SIGN}' ]
},
function(req, res) {
res.say('Things are looking up today for ' + req.get('SIGN') + '.');
}
);This intent can be interacted with like this:
> chatskills, ask horoscope for Scorpio
Things are looking up today for Scorpio.
When a user provides input, the input is matched against each skill and their list of intents. When a match is found, a new session starts, and the skill begins executing.
When a session has started for a user, the activated skill's intent can get/set variable values within the session. This allows you to store and retrieve data.
While a session is open for a user, all input from the user is directed to the activated skill. In this manner, the user does not need to re-request a skill ("chatskills, ask hello to say hi"). Instead, the user can simply provide text, which will be matched against the currently executing skill's intents.
An intent can keep a session open by returning true and end a session by returning false. An intent may also omit a return statement, which is the same as returning false.
For an example using session, see the horoscope skill. Notice, the intent asks the user a question and then returns true to keep the session going. The intent only returns false once a valid response is given, thus, ending the session.
In summary, when a user session is open, all input from the user is directed to the skill. When a user session is ended, input from the user must be received in the format, "chatskills, ask [SKILL] text", to execute a new skill.
The default session timeout is 1 hour of no input from the user. To change the session timeout, set chatskills.timeout = 3600, where the value is specified in seconds. To disable session timeout, set the value to 0.
The default chatbot name is "chatskills". All requests to execute a skill must begin with the chatbot name. For example, "chatskills, ask hello to say hi". To customize the chatbot name, use the following:
chatskills.name('awesome');To display warnings and errors, set chatskills.verbose = true.
Chatskills uses alexa-app to generate many sample utterances from your intents. For a more detailed description of utterances, see here.
Pass an object with two properties: slots and utterances.
app.intent('sampleIntent',
{
"slots":{"NAME":"LITERAL","AGE":"NUMBER"},
"utterances":[ "my {name is|name's} {names|NAME} and {I am|I'm} {1-100|AGE}{ years old|}" ]
},
function(request,response) { ... }
);The slots object is a simple Name:Type mapping. The type must be one of Amazon's supported slot types: LITERAL, NUMBER, DATE, TIME, DURATION
The utterances syntax allows you to generate many (hundreds or even thousands) of sample utterances using just a few samples that get auto-expanded. Any number of sample utterances may be passed in the utterances array. Below are some sample utterances macros and what they will be expanded to.
"my favorite color is {red|green|blue|NAME}"
=>
"my favorite color is {red|NAME}"
"my favorite color is {green|NAME}"
"my favorite color is {blue|NAME}"
This lets you define multiple ways to say a phrase, but combined into a single sample utterance
"{what is the|what's the|check the} status"
=>
"what is the status"
"what's the status"
"check the status"
When capturing a numeric slot value, it's helpful to generate many sample utterances with different number values
"buy {2-5|NUMBER} items"
=>
"buy {two|NUMBER} items"
"buy {three|NUMBER} items"
"buy {four|NUMBER} items"
"buy {five|NUMBER} items"
Number ranges can also increment in steps
"buy {5-20 by 5|NUMBER} items"
=>
"buy {five|NUMBER} items"
"buy {ten|NUMBER} items"
"buy {fifteen|NUMBER} items"
"buy {twenty|NUMBER} items"
"what is your {favorite |}color"
=>
"what is your color"
"what is your favorite color"
Several intents may use the same list of possible values, so you want to define them in one place, not in each intent schema. Use the app's dictionary.
app.dictionary = {"colors":["red","green","blue"]};
...
"my favorite color is {colors|FAVEORITE_COLOR}"
"I like {colors|COLOR}"
MIT
Kory Becker http://www.primaryobjects.com/kory-becker