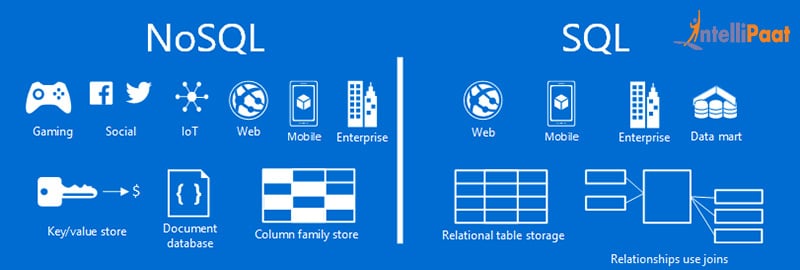
The battle of ease between SQL and NOSQL
MongoDB is an open-source document database and leading NoSQL database. MongoDB is written in C++. This lesson will give you great understanding on MongoDB concepts needed to create and deploy a highly scalable and performance-oriented database.
- Schema less − MongoDB is a document database in which one collection holds different documents. Number of fields, content and size of the document can differ from one document to another.
- Structure of a single object is clear.
- No complex joins.
- Deep query-ability. MongoDB supports dynamic queries on documents using a document-based query language that's nearly as powerful as SQL.
- Tuning.
- Ease of scale-out − MongoDB is easy to scale.
- Conversion/mapping of application objects to database objects not needed.
- Uses internal memory for storing the (windowed) working set, enabling faster access of data.
- Document Oriented Storage − Data is stored in the form of JSON style documents.
- Index on any attribute
- Replication and high availability
- Auto-sharding
- Rich queries
Big Data, Content Management and Delivery, Mobile and Social Infrastructure, User Data Management, Data Hub
For Windows Users visit this link
-
Open the Terminal app and type brew update.
-
After updating Homebrew brew install mongodb
-
After downloading Mongo, create the “db” directory. This is where the Mongo data files will live. You can create the directory in the default location by running
mkdir -p /data/db -
Make sure that the /data/db directory has the right permissions by running
-
sudo chown -Rid -un/data/db
# Enter your passwordRun the Mongo daemon, in one of your terminal windows run mongod. This should start the Mongo server. Run the Mongo shell, with the Mongo daemon running in one terminal, type mongo in another terminal window. This will run the Mongo shell which is an application to access data in MongoDB.
- To exit the Mongo shell run
quit() - To stop the Mongo daemon hit
ctrl-c
As said earlier MongoDB is Schemaless but to make data consistent we need mongoose.
Just like in Rails, we can use mongoose to create models so that the controller can access the models to enusure data integrity.
(Mongoose Docs)[https://mongoosejs.com/docs/index.html]
To start mongodb run mongod
lets start off by install mongoose in our node application.
$ npm install mongoose --save var mongoose = require('mongoose');
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var blogSchema = new Schema({
title: String,
author: String,
body: String,
comments: [{ body: String, date: Date }],
date: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
hidden: Boolean,
meta: {
votes: Number,
favs: Number
}
});
Fields can have any of the following data types:
- String
- Number
- Date
- Buffer
- Boolean
- Mixed
- ObjectId
- Array
var blogSchema = new Schema({
title: String,
author: String,
body: String,
comments: [{ body: String, date: Date }],
date: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
hidden: Boolean,
meta: { //embedded Object
votes: Number,
favs: Number
}
},{timestamps: true});
const Blog = mongoose.model('Blog', blogSchema);
module.exports = Blog;In Class Lab Mongoose Lab
npm install mongoose- Inside server.js:
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
//... and then farther down the file
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/basiccrud', { useNewUrlParser: true});
mongoose.connection.once('open', ()=> {
console.log('connected to mongo');
});mkdir modelstouch models/fruits.js- Create the fruit schema
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const fruitSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: { type: String, required: true },
color: { type: String, required: true },
readyToEat: Boolean
});
const Fruit = mongoose.model('Fruit', fruitSchema);
module.exports = Fruit;Inside server.js:
const Fruit = require('./models/fruits.js');
//... and then farther down the file
app.post('/fruits/', (req, res)=>{
if(req.body.readyToEat === 'on'){ //if checked, req.body.readyToEat is set to 'on'
req.body.readyToEat = true;
} else { //if not checked, req.body.readyToEat is undefined
req.body.readyToEat = false;
}
Fruit.create(req.body, (error, createdFruit)=>{
res.send(createdFruit);
});
});app.get('/fruits', (req, res)=>{
res.send('index');
});touch views/index.ejs
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Fruits index page</h1>
</body>
</html>Render the ejs file
app.get('/fruits', (req, res)=>{
res.render('index.ejs');
});app.get('/fruits', (req, res)=>{
Fruit.find({}, (error, allFruits)=>{
res.render('index.ejs', {
fruits: allFruits
});
});
});Update the ejs file:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Fruits index page</h1>
<ul>
<% for(let i = 0; i < fruits.length; i++){ %>
<li>
The <%=fruits[i].name; %> is <%=fruits[i].color; %>.
<% if(fruits[i].readyToEat === true){ %>
It is ready to eat
<% } else { %>
It is not ready to eat
<% } %>
</li>
<% } %>
</ul>
</body>
</html>Add a link to the create page:
<nav>
<a href="/fruits/new">Create a New Fruit</a>
</nav>Inside the create route
Fruit.create(req.body, (error, createdFruit)=>{
res.redirect('/fruits');
});<li>
The
<a href="/fruits/<%=fruits[i].id; %>">
<%=fruits[i].name; %>
</a>
is <%=fruits[i].color; %>.
<% if(fruits[i].readyToEat === true){ %>
It is ready to eat
<% } else { %>
It is not ready to eat
<% } %>
</li>app.get('/fruits/:id', (req, res)=>{
Fruit.findById(req.params.id, (err, foundFruit)=>{
res.send(foundFruit);
});
});touch views/show.ejs- Add HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Fruits show page</h1>
The <%=fruit.name; %> is <%=fruit.color; %>.
<% if(fruit.readyToEat === true){ %>
It is ready to eat
<% } else { %>
It is not ready to eat
<% } %>
<nav>
<a href="/fruits">Back to Fruits Index</a>
</nav>
</body>
</html>Render the ejs
app.get('/fruits/:id', (req, res)=>{
Fruit.findById(req.params.id, (err, foundFruit)=>{
res.render('show.ejs', {
fruit:foundFruit
});
});
});(Start Driver Management)[driver.md]