Just another API testing library.
ApiRock is a fluent Haxe library you can use to test HTTP based REST services.
Example:
new ApiRock("Postman Echo") // Create your test using 'Fluent Interface'
.makeRequest('Get a simple request') // Add a test cases
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/get')
.sendQueryStringData('foo', 'bar')
.mustPass()
.makeDataAsserts({args:{foo:'bar'}})
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing received headers') // Add another test...
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/response-headers')
.sendQueryStringData('foo', 'bar')
.mustPass()
.makeHeadAsserts({foo:'bar'})
.then()
.runTests(); // then RUN!ApiRock is a stack of activities. After you write your group of activities, ApiRock will run everything in order. If something goes wrong, the test will end with an error.
ApiRock makes an API requests and makes sure everything is OK.
new ApiRock("Google Request")
.makeRequest('Get Google Page')
.GETting('https://www.google.com')
.mustPass()
.then()
.runTests();makeRequest(why:StringKeeper)
| Params | Description |
|---|---|
| why | Explain why you need this request |
If you need wait a while between activities, use the Wait Activity.
new ApiRock("Wait Test")
.makeRequest('Get a simple request')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/get')
.mustPass()
.then()
.waitFor(5, WaitActivityMeasure.SECONDS)
.then()
.makeRequest('Get another request after 5 seconds')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/get')
.mustPass()
.then()
.runTests();waitFor(time:Int, ?measure:WaitActivityMeasure)
| Params | Description |
|---|---|
| time | The amount of time to wait |
| measure | The unity of time. Can be Hour, Minutes or Seconds (default) |
Use this activity if you need to clear all data stored on StringKeeper.
clearStringKeeper()
If you need to execute some very specific tasks, use Custom Activities.
new ApiRock('Custom Test')
.customActivity(
function (print:String->Void):Void {
if (true) print('True is True!');
else throw 'Something wrong with bools!';
}
)
.then()
.runTests();StringKeeper is a special kind of String. You can use #hash values on string that will be replaced by a value in the future.
Example:
// Seting a StringKeeper
var foo:StringKeeper = 'Foo value is #value';
trace(foo); // print 'Foo value is #value'
// ...later in the code
StringKeeper.addData('value', 'bar');
trace(foo); // print 'Foo value is bar'
// ...and other change
StringKeeper.addData('value', 'none');
trace(foo); // print 'Foo value is none'
// cleaning StringKeeper data
StringKeeper.clear();
trace(foo); // print 'Foo value is #value'StringKeeper.addData(key:String, value:String):Void
StringKeeper.getData(key:String):Void
StringKeeper.clear():Void
macbook:~ export MY_VALUE=testvar foo:StringKeeper = 'Sys Value: #MY_VALUE'; trace(foo); // print 'Sys Value: test'
There is 5 moments to create a good request test.
- Set the request Method
- Organize the data and headers to send
- Tell if the request must be a success, fail or result a particular status code
- Validate the received data and headers
- Keep some data in memory for future requests
You can choose one of those 5 predefined methods...
POSTing(url:StringKeeper)
GETting(url:StringKeeper)
DELETing(url:StringKeeper)
PUTting(url:StringKeeper)
PATCHing(url:StringKeeper)
... or write your own using this:
requesting(url:StringKeeper, method:StringKeeper)
new ApiRock('Methods Tests')
.makeRequest('Testing GET method')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/your/cool/api')
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing POST method')
.POSTing('http://localhost:8080/your/cool/api')
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing DELETE method')
.DELETing('http://localhost:8080/your/cool/api')
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing PUT method')
.PUTting('http://localhost:8080/your/cool/api')
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing PATCH method')
.PATCHing('http://localhost:8080/your/cool/api')
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing OTHER method')
.requesting('http://localhost:8080/your/cool/api', 'OTHER')
.then()
.runTests();After set up your URL and request method, add some data to request.
sendingHeader(head:StringKeeper, value:StringKeeper)
Add headers to you request:
new ApiRock('Send Header Tests')
.makeRequest('Testing sending headers')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/headers')
.sendingHeader('foo1', 'bar1')
.sendingHeader('foo2', 'bar2')
.then()
.runTests();BONUS: The method sendingBasicAUTH adds a special header following the Basic AUTH rules: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Basic_access_authentication
.makeRequest('Testing basic authentication')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/basic-auth')
.sendingBasicAUTH('postman', 'password')
.then()sendingQueryStringData(key:StringKeeper, value:StringKeeper)
Add query string data:
apirock.makeRequest('Get a simple request')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/get')
.sendingQueryStringData('foo', 'bar value') // This will append '?foo=bar%20value' to URL.
.then() // Complete URL: https://postman-echo.com/get?foo=bar%20value
apirock.makeRequest('Get a simple request')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/get?x=0') // Combine query parameter at url are allowed.
.sendingQueryStringData('y', '5') // This will append '&y=5&z=3' to URL.
.sendingQueryStringData('z', '3') // Complete URL: https://postman-echo.com/get?x=0&y=5&z=3
.then()
apirock.makeRequest('Get a simple request')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/get') // If you repeat the same key name, it will be converted to an array
.sendingQueryStringData('arr', '5') // This will append '?arr[]=5&arr[]=3' to URL.
.sendingQueryStringData('arr', '3') // Complete URL: https://postman-echo.com/get?arr[]=5&arr[]=3
.then()
There is 3 methods to include request body data. You can choose only one of them per request:
sendingFormData(fieldName:StringKeeper, fieldValue:StringKeeper)
Send value as form field values. If you don't set any content-type header, ApiRock sends automatically the value application/x-www-form-urlencoded.
.makeRequest('Send form data')
.POSTing('https://postman-echo.com/post')
.sendingFormData('foo1', 'bar1') // The request body will be 'foo1=bar1&foo2=bar2'
.sendingFormData('foo2', 'bar2')
.then()
.makeRequest('Send form data')
.POSTing('https://postman-echo.com/post') // If you repeat the same key name, it will be converted to an array
.sendingFormData('foo', 'bar1') // The request body will be 'foo[]=bar1&foo[]=bar2'
.sendingFormData('foo', 'bar2')
.then()sendingJsonData(data:StringKeeper)
Send the value as Json. If you don't set any content-type header, ApiRock sends automatically the value application/json.
.makeRequest('Send json data')
.POSTing('https://postman-echo.com/post')
.sendingJsonData(haxe.Json.stringify({foo:'bar'}))
.then()sendingRawData(data:StringKeeper, ?contentType:StringKeeper = 'text/plain')
If you want to send raw data, use this method. The default content-type for this method is text/plain.
.makeRequest('Send raw data')
.POSTing('https://postman-echo.com/post')
.sendingRawData('raw data')
.then()mustPass()
This is the default expected status code. ApiRock consider a SUCCESS any status code from 200 to 299.
mustFail()
ApiRock consider a FAILURE any status code above 300.
mustDoCode(?code:Int = 200)
ApiRock expects the exact status code.
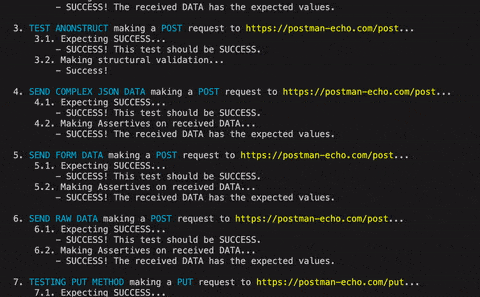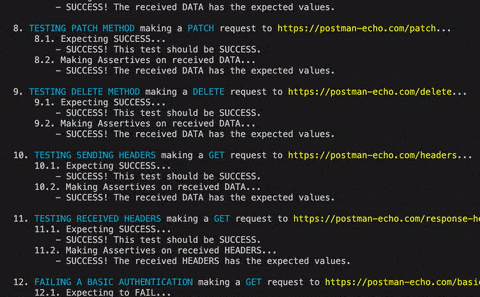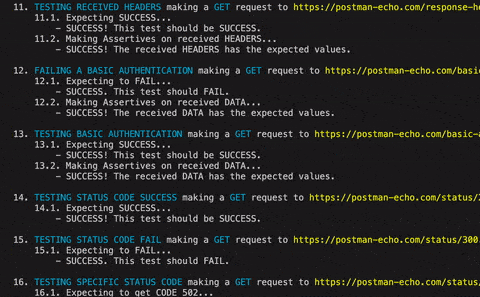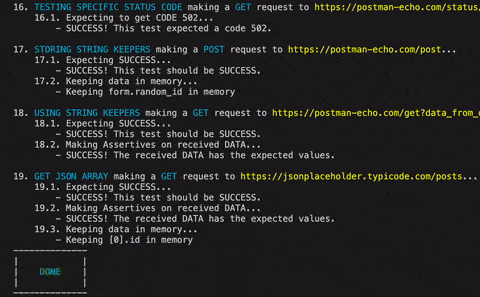
.makeRequest('Testing status code SUCCESS')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/status/200')
.mustPass()
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing status code FAIL')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/status/300')
.mustFail()
.then()
.makeRequest('Testing specific status code')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/status/502')
.mustDoCode(502)
.then().makeRequest('Testing received headers')
.GETting('https://postman-echo.com/response-headers')
.makeHeadAsserts({'content-type':'application/json; charset=utf-8'})
.then()ApiRock uses AnonStruct lib to validate response data.
More Info:
Assume that the GET request to http://localhost:8080/user/profile returns JSON as:
{
"name" : "John Smith",
"email" : "[email protected]",
"birthday" : "04/04/1982"
}If you need to test only the data structure (not the values), first you need create a new AnonStruct validator class:
private class ValidateUserProfile extends AnonStruct {
public function new() {
super();
this.propertyString('name')
.refuseEmpty()
.refuseNull();
this.propertyString('email')
.refuseEmpty()
.refuseNull();
this.propertyDate('birthday')
.refuseNull();
}
}... and then pass the Class reference to expecting(anon:Class<AnonStruct>) method:
.makeRequest('Test AnonStruct')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/profile')
.mustPass()
.expecting(ValidateUserProfile)
.then()There is a lot of way to make data asserts using ApiRock.
Assume that the GET request to http://localhost:8080/user/cars returns JSON as:
{
"name" : "John Smith",
"age" : 37,
"cars": [
{ "name" : "Ford",
"models" : [
{"name":"Fiesta", "colors":["Pearl", "Silver"]},
{"name":"Focus", "colors":["Blue", "Black"]},
{"name":"Mustang", "colors":["Silver", "Blue"]}
]
},
{ "name" : "BMW",
"models" : [
{"name":"320", "colors":["Bright Yellow"]},
{"name":"X3", "colors":["Titan Silver"]},
{"name":"X5", "colors":["Black", "Beige"]}
]
},
{ "name" : "Fiat",
"models" : [
{"name": "500", "colors" : ["Bianco", "Rosso"]},
{"name" : "Panda", "colors" : ["Bianco", "Ivory"]}
]
}
]
}Tests if name is "John Smith" and age is 37:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/cars')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
age : 37,
name : "John Smith"
}
)
.then()Tests if cars has all the expected values:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/cars')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
"cars": [
{ "name" : "Ford",
"models" : [
{"name":"Fiesta", "colors":["Pearl", "Silver"]},
{"name":"Focus", "colors":["Blue", "Black"]},
{"name":"Mustang", "colors":["Silver", "Blue"]}
]
},
{ "name" : "BMW",
"models" : [
{"name":"320", "colors":["Bright Yellow"]},
{"name":"X3", "colors":["Titan Silver"]},
{"name":"X5", "colors":["Black", "Beige"]}
]
},
{ "name" : "Fiat",
"models" : [
{"name": "500", "colors" : ["Bianco", "Rosso"]},
{"name" : "Panda", "colors" : ["Bianco", "Ivory"]}
]
}
]
}
)
.then()Tests if cars[1] (cars at index 1) has an object with name equals to BWM and test if cars[2] has name equals to Fiat:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/cars')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
"cars[1]" : {"name":"BMW"},
"cars[2]" : {"name":"Fiat"}
}
)
.then()Tests if the first model (model[0]) of the first car (car[0]) has the name equals to Fiesta:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/cars')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
"cars[0]" : {"models[0]" : {"name": "Fiesta"}}
}
)
.then()Tests if there is ANY car element (cars[?]) with the nameequals to Fiat:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/cars')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
"cars[?]" : {"name":"Fiat"}
}
)
.then()Tests if there is any model of any cars with Ivory value at index 1 of colors array:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/user/cars')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
"cars[?]" : {"models[?]": {"colors[1]":"Ivory"}}
}
)
.then()
SPECIAL CASE: When the root object is an array!
If the received data is an Array, for example...
[
{"name" : "red", "color" : "#FF0000"},
{"name" : "green", "color" : "#00FF00"},
{"name" : "blue", "color" : "#0000FF"},
]...and you want assert only some elements, you can do like this:
.makeRequest('Asserting Data')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/color/list')
.makeDataAsserts(
{
"[1]" : {name : "green"},
"[2]" : {color : "#0000FF"}
}
)
.then()Keepers are used to store some information in memory to be used in any future requests.
keepingData(property:String, key:String)
Let's say you request a list of books and then need to get some info about the author using the id:
[
{
"book_id" : 8984,
"author_id" : 789,
"author" : "Jane Austen",
"title" : "Pride and Prejudice"
},
{
"book_id" : 5632,
"author_id" : 6372,
"author" : "Giovanni Boccaccio",
"title" : "The Decameron",
},
...
]It's possible to get only the author_id of the first item of the array.
.makeRequest('Request Book List')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/book/list')
.keepingData('[0].author_id', 'keep_author_id')
.then()Then, in the next request, you can use the keep_author_id in the url...
.makeRequest('Request Book List')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/author/#keep_author_id') // the url will be converted to http://localhost:8080/author/789 in the future.
.mustPass()
.then()...or any other StringKeeper objetct:
.makeRequest('Request Book List')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/author')
.sendingFormData('author_id', '#keep_author_id') // the value will be converted to "789" in the future.
.mustPass()
.then()keepingHeader(header:String, key:String)
You can keep response headers values and works just like keeping data.
.makeRequest('Request Book List')
.GETting('http://localhost:8080/book/list')
.keepingHeader('some-special-header', 'specialHeader')
.then()The file test\ApiRockTest.hx contains a lot of examples.
To build this examples, clone the ApiRock git repository and:
> haxe examples.hxmland run...
> neko build/example.nDEBUG MODE
Build your haxe code using -D debug:
> haxe examples.hxml -D debug